Multiplication Centers
Fluency with basic multiplication facts (0x0 - 9x9) and related division facts is considered foundational for further advancement in mathematics. These facts form the basis for learning multi-digit multiplication and division, area, fractions, percentages, volume, ratios, and decimals. This page provides examples of multiplication centers that can be used to support the development of multiplication fluency. These centers can be used by teachers or parents to support students' progress within a stage, or to facilitate movement to the next stage on the multiplication continuum. For more information on using math fluency centers as an ongoing classroom routine see here. For division centers see here.
Stage 1.0
These students can make equal groups using a count by ones strategy.
Next Steps:
- Begin to see a group as one unit
- Use skip counting or repeated addition to find products
- Build arrays to solve multiplication problems
Possible Centers:
Relate Addition and Multiplication
Counting Collections (ver.6)
Equal Groups
Word Problems: Arrays (Set 1)
Stage 1.1
These students see a group as one unit. They can use skip counting or repeated addition to find products.
Next Steps:
- Use thinking strategies to multiply by 5 and 10 (e.g. Use Tens)
- Develop an understanding of rules for multiplying by 1 and 0
Possible Centers:
Multiples of 5
Multiplication Bump (x5)
Find the Facts (x5)
Multiplication Squares (x5/x10)
For more Centers aligned with Stage 1.1 see this document.
Stage 1.2
These students demonstrate fluent use of thinking strategies when multiplying by 5 and 10 (Use Tens). They understand rules for multiplying by 0 and 1.
Next Steps:
- Use thinking strategies to multiply by 2, 4, and 8 (e.g. Use Doubles, Use the Commutative Property)
Possible Centers:
Multiplication Bump (x2)
Use Doubles (x4/x8)
Find the Facts (x4)
Find the Facts (x8)
Google Slides:
Multiples of 2
Multiples of 8
For more Centers aligned with Stage 1.2 see this document.
Stage 1.3
These students demonstrate fluent use of thinking strategies when multiplying by 2, 4, and 8 (Use Doubles, Use the Commutative Property)
Next Steps:
- Use thinking strategies to multiply by 3, 6, 7 and 9 (e.g. Build up/Build Down, Use the Commutative Property)
Possible Centers:
Multiples of 3
Consecutive Products (x6)
Consecutive Products (x9)
Find the Facts (x9)
Consecutive Products (x 6)
Consecutive Products (x9)
For more Centers aligned with Stage 1.3 see this document.
Stage 1.4
These students demonstrate fluent use of thinking strategies when multiplying by a single digit factor (x0 -x9).
Next Steps:
- Continue to regularly practice thinking strategies for x0 - x9 facts in order to know from memory all products of two one-digit numbers
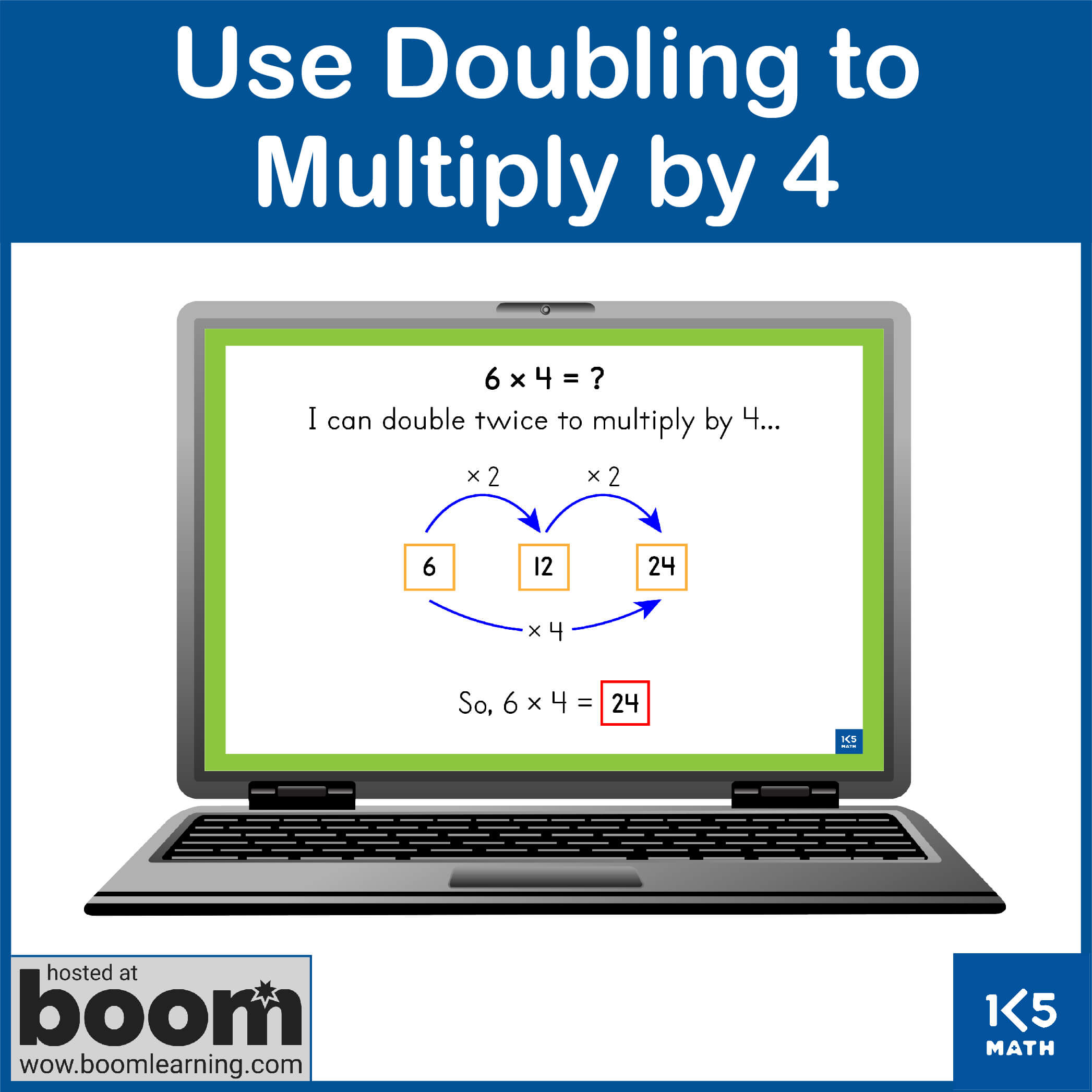
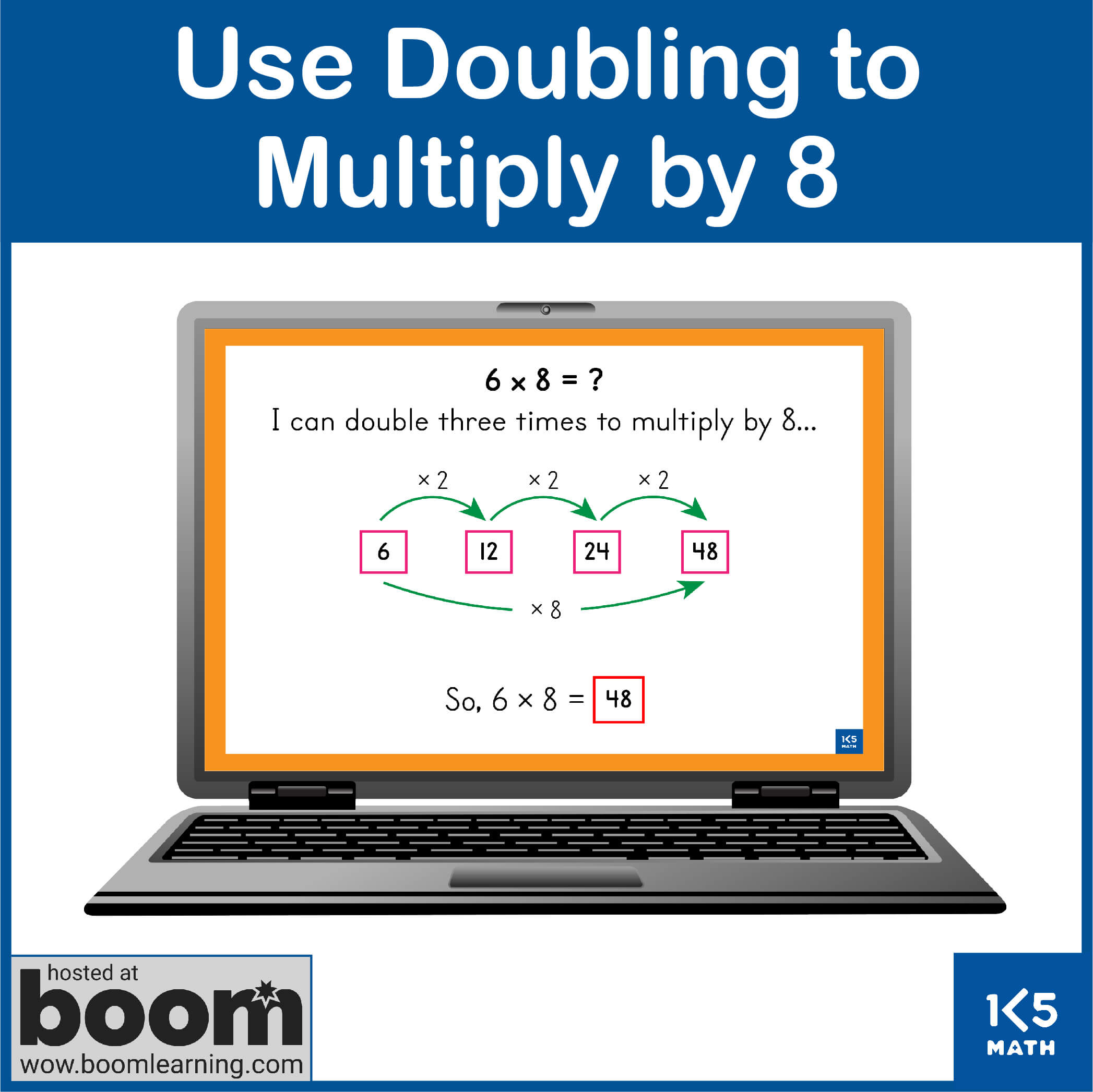
- Use thinking strategies for x2-x9 to solve problems involving extended facts within 100 (e.g. solve 16 x 4 by
thinking 'Double 16 is 32. Double 32 is 64. So, 16 x 4 = 64)
Possible Centers:
4 in a Line on a Multiplication Chart
Multiply by 4 (extended facts)
Google Slides:
4 in a Line on a Multiplication Chart
For more Centers aligned with Stage 1.4 see this document.
Stage 1.5
These students demonstrate fluent use of thinking strategies when solving problems involving extended facts within 100.
Next Steps:
- Multiply one-digit numbers by a multiple of 10 using place value knowledge (e.g. 6 x 50 = 6 x 5 tens = 30 tens = 300)
Possible Centers:
Multiply One-Digit Numbers by Multiples of Ten
For more Centers aligned with Stage 1.5 see this document.
Stage 2.1
These students demonstrate fluency with basic multiplication facts and can multiply one-digit numbers by a multiple of 10 (e.g. 6 x 50, 8 x 40).
Next Steps:
- Multiply a 3-digit number by a 1-digit number (with and without regrouping) using strategies based on place value. Illustrate and explain the calculation using equations, rectangular arrays, and/or area models.
Possible Centers:
Multiplication Race (1 x 3-digit)
Make the Largest Product (3 x 1-digit)
Google Slides:
Multiplication Race (1 x 3-digit)
Make the Largest Product (3 x 1-digit)
For more Centers aligned with Stage 2.1 see this document.
Stage 2.2
These students fluently multiply a 3-digit number by a 1-digit number (with and without regrouping) using strategies based on place value. They illustrate and explain the calculation using equations, rectangular arrays, and/or area models.
Next Steps:
- Multiply a 4-digit number by a 1-digit number (with and without regrouping) using strategies based on place value. Illustrate and explain the calculation using equations, rectangular arrays, and/or area models.
Possible Centers:
Make the Smallest Product (4 x 1-digit)
Multiplication Target Number (ver. 2)
Google Slides:
Make the Smallest Product (ver.2)
For more Centers aligned with Stage 2.2 see this document.
Stage 2.3
These students fluently multiply a 4-digit number by a 1-digit number (with and without regrouping) using strategies based on place value. They illustrate and explain the calculation using equations, rectangular arrays, and/or area models.
Next Steps:
- Multiply a 2-digit number by a 2-digit number using strategies based on place value. Illustrate and explain the calculation using equations, rectangular arrays, and/or area models.
Possible Centers:
Make the Smallest Product (2 x 2-digit)
Multiplication Target Number (ver. 3)
Google Slides:
Multiplication Tic-Tac-Toe (ver. 3)
For more Centers aligned with Stage 2.3 see this document.
Stage 3.1
These students fluently multiply a 2-digit number by a 2-digit number (with and without regrouping) using strategies based on place value. They illustrate and explain the calculation using equations, rectangular arrays, and/or area models.
Next Steps:
- Multiply a 3-digit number by a 2-digit number using a standard algorithm.
Possible Centers:
Make the Largest Product (3 x 2-digit)
Double and Halve (3 x 2-digit)
Google Slides:
Multiplication Race (2 x 3-digit)
For more Centers aligned with Stage 3.1 see this document.
Stage 3.2
These students fluently multiply a 3-digit number by a 2-digit number (with and without regrouping) using a standard algorithm.
Next Steps:
- Multiply a 4-digit number by a 2-digit number using a standard algorithm.
Possible Centers:
Multiplication Tessellation (4 x 2-digit)
Multiplication Tic-Tac-Toe (ver. 5)
For more Centers aligned with Stage 3.2 see this document.
Stage 3.3
These students fluently multiply a 4-digit number by a 2-digit number (with and without regrouping) using a standard algorithm.
Next Steps:
- Multiply a 3-digit number by a 3-digit number using a standard algorithm.
Possible Centers:
Multiplication Tessellation (3 x 3-digit)
Multiplication Tic-Tac-Toe (ver. 6)
For more Centers aligned with Stage 3.3 see this document.